If you’re on a small nonprofit team, you already know two things: time is short, and expectations are high. This guide is a practical playbook for organic social media growth that respects both realities. No magic shortcuts. No vague lists of “post more.” Instead: a system you can implement a little at a time, scale with capacity, and measure for steady, sustainable impact.
This is written for teams doing nonprofit social media marketing — not agencies selling services. It treats social media as a program tool, tied to fundraising, volunteer recruitment, advocacy, and community-building. Read it as a realistic social media strategy for nonprofits that you can start using tomorrow and refine over months.
What “organic growth” actually means for nonprofits
Organic growth is growth that comes from genuine audience interest — follows, shares, comments, visits, and measurable actions like email sign-ups or donations — without paying directly for reach. For nonprofits, organic social media growth for nonprofits looks like a growing community that trusts you enough to donate, volunteer, or advocate. It’s not vanity metrics; it’s a pipeline of people who move from awareness → engagement → action.
Prioritizing community over quick asks is central: the long-term returns (donor retention, volunteer recruitment, policy influence) come from repeated, human interactions more often than from a single viral moment. If you want the full framework, see the pillar guide on the complete guide on nonprofit social media marketing for how these pieces fit together.
Why organic growth is harder in 2026 — and what that means for you
Algorithms favor content that creates two things: meaningful engagement and retention. Platforms are saturated. Short-form trends burn quickly. Attention is fragmenting across more formats and apps. At the same time, people are more skeptical of organizations. That raises the bar: you must do fewer things very well.
What this means for nonprofits:
Quality over quantity — inconsistent posting hurts momentum more than slow, steady posting.
Community-first content — content that invites participation and repeat visits wins.
Systems beat hacks — reliable processes (story pipelines, repurposing systems, engagement routines) matter more than chasing trends.
This is the practical context for any social media strategy for nonprofits. Focus on systems that fit your capacity and mission rather than chasing every new feature.
Why most nonprofits fail at organic growth (and how you avoid the same traps)
Common failure modes:
No clear audience — treating “everyone” as the audience.
Random content — posting whenever there’s something to post.
One-way broadcasting — posting but not responding to comments or messages.
Metrics that don’t matter — celebrating follower counts without tracking email sign-ups, volunteer interest, or donations.
Burnout-first strategy — expecting a founder/volunteer to do everything.
How to avoid them:
Define 1–2 primary audience segments (donors, volunteers, community members).
Use a content plan with repeatable frameworks (see later).
Set an engagement routine: 15–30 minutes daily to respond, 1–2 focused blocks weekly for content creation.
Track outcome KPIs (email sign-ups, event RSVPs, small donations) alongside social KPIs.
If you’re short on time, start by aligning one conversion (for example, email sign-ups) to one repeating post format. This simple trade reduces overwhelm and connects social activity to real program outcomes.
A simple model of platform algorithms (no jargon)
Think of platform algorithms like two basic filters:
Does this post create an immediate small-group reaction? (likes, saves, replies)
Do those reactions lead people to spend more time on the platform with the content?
If both are “yes,” platforms show your content to more people. So your job is to create content that invites quick, real reactions and encourages people to stay engaged (watch full video, click to comment, share with a friend).
Practical takeaways:
Ask for a specific reaction (answer a question, tag someone).
Make the first 2–3 seconds count on video or the first line count in a caption.
Keep content scannable for mobile-first users.
This model should shape your nonprofit social media marketing decisions more than chasing platform updates.
The nonprofit organic growth system — Three pillars
- Engagement-first content
- Storytelling systems that compound
Community and partnership growth
These pillars form a unified framework. Think of them as parts of your social media strategy for nonprofits: content that creates engagement, stories that build trust over time, and partnerships that amplify reach.
Pillar 1 — Engagement-first content
Engagement-first means you design each post to generate a meaningful response, not just impressions.
Repeatable content frameworks
Use 3–4 formats repeatedly so your audience learns what to expect.
Story → Insight → Micro-ask
Story: 30–60 seconds (video) or 150–250 words (caption) about one person or outcome.
Insight: What this taught you about your mission.
Micro-ask: A non-transactional ask (share, comment, sign up for a newsletter).
Example: “When Fatima showed up to the kitchen, she said X. We learned Y. If this matters to you, share this story with someone who cares.”
Behind-the-Scenes Mini-Series
Short recurring posts that show process, staff/volunteer routines, or program days. Series builds habit and repeat views.
Question-to-Conversation
One-line question + photo. High comment potential. Use polls and stories to follow up.
Impact Snapshot (Data + Human)
A simple stat paired with a beneficiary quote. Use sparingly and always humanize the number.
Repeatable frameworks support consistent social media management for nonprofits by reducing decision fatigue and making batch production practical.To streamline this process, using one of the 7 Best Social Media Management Tools for Nonprofits can help you schedule posts in advance and manage your entire workflow efficiently.
Tactical engagement moves (ethical, low-effort)
Pin a single “How to Help” post so newcomers know the next step.
Use captions that ask for specific responses (e.g., “Reply with one word if you agree”).
Highlight commenters in Stories or replies to boost repeat interaction.
Encourage user-generated content with a clear prompt and a simple hashtag.
Pillar 2 — Storytelling systems that compound over time
Stories are your single best long-term asset. But to compound, they must be organized.
Build a “story bank”
Create and tag a shared folder with short bios, photos, captions, recorded 60–90 second videos, and permissions. Tag by theme: donor story, volunteer profile, program day, challenge. This reduces decision fatigue and maintains ethical record-keeping.
Create narrative arcs
Think in arcs, not one-offs:
Problem → Intervention → Outcome → Next step
Run these arcs as mini-campaigns over 2–6 weeks with consistent CTAs (newsletter sign-up, volunteer form).
Compound effect: repeated arcs build recognition and trust — donors and partners act when they’ve seen the same problem and solution told multiple times from different angles.
Ethics and consent
Always get written consent for storytelling. Have a simple form that explains usage, duration, and opt-out. This protects people and your reputation.
Pillar 3 — Community and partnership growth
Organic growth scales when other communities amplify your work.
Partnerships that move the needle
Local organizations: co-host livestreams, share each other’s success stories.
Micro-influencers: volunteers and local advocates often have engaged followings and want mission-aligned content.
Peer organizations: cross-promote resources (not donors). Collaboration is high-signal and low-cost.
Facilitate community, don’t just broadcast
Run small cohort groups (Facebook group, WhatsApp, or an email cohort) for active volunteers and donors. Use these groups to pilot content and gather feedback.
Host recurring live Q&A or program tours. Lives generate higher engagement and repeat attendance.
These tactics help your nonprofit social media marketing move from one-off posts to a supportive ecosystem that sustains action.
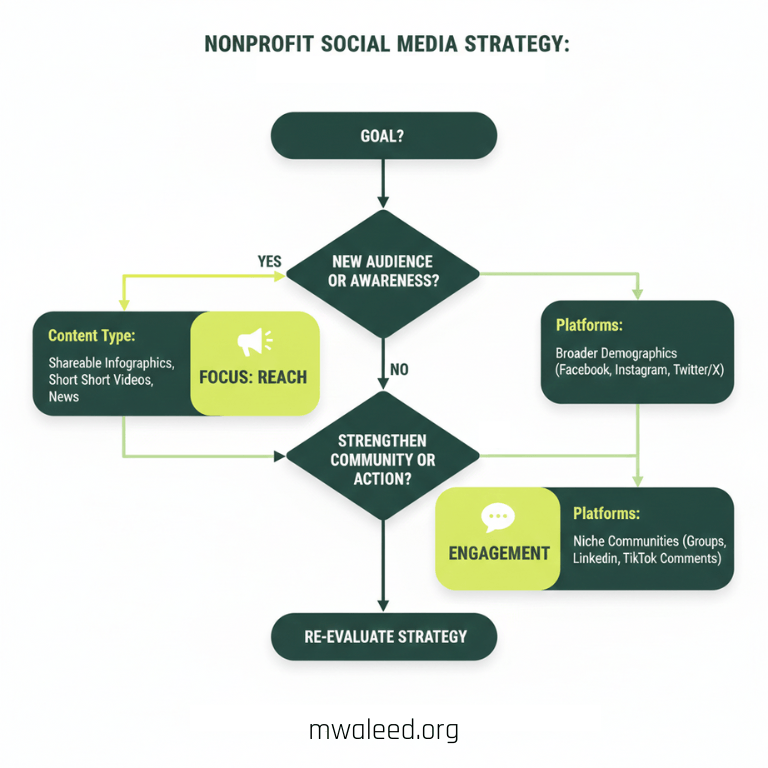
Platform- and format-specific notes (practical)
- Short video: Most platforms reward completed views. Hook viewers in the first 2–3 seconds. Add captions for sound-off viewing.
Carousels / multi-image posts: Great for process or before/after impact. Each slide should add value.
Stories / ephemeral content: Use for real-time updates and CTAs; they build familiarity.
Threads / long-form posts: Use for policy explanations or deep dives; convert into shorter clips for discovery.
LinkedIn: Use for program impact, funding appeals to corporate partners, and staff thought leadership.
Email + social synergy: Social drives sign-ups; email strengthens relationships. Always include a simple newsletter CTA in social bios and a pinned post.
Pick 1–2 formats your team can do well, then repurpose that content intelligently. This is the core of effective social media management for non profits.
Capacity-based strategy — what to do depending on team size
Volunteer or solo manager
Focus: 3 posts/week on one priority platform + daily 15-minute engagement window.
Content: one weekly story post, one impact snapshot, one question or call for help.
Systems: 30-minute weekly content block for batching.
Small team (2–4 people)
Focus: 4–6 posts/week across two platforms. Add short video and repurposing.
Content: monthly mini-series, weekly volunteer highlight, biweekly live or Q&A.
Systems: shared calendar, story bank, monthly reporting review.
Staffed team (4+)
Focus: platform-tailored content, community management, and tactical paid amplification when necessary.
Content: multi-episode series, partnerships, supporter cohorts.
Systems: editorial calendar, CRM integration, A/B tests on CTAs.
If posting and community care are draining staff time, consider bringing in professional support. A nonprofit social media manager can set up the systems and train your team. For larger needs, social media management for nonprofits is a role that can be filled part-time or by a specialist agency.
Organic reach vs paid amplification — when to mix
Organic builds trust and community; paid amplifies specific asks or critical awareness moments.
Use paid when:
You need to drive urgent conversion (event sign-ups, campaign deadlines).
You want to seed a new content series to jump-start reach.
You’re testing which messages move people to action (small audience tests).
Keep most ongoing messaging organic, and use paid tactically to boost high-performing content. Paid works best when it amplifies content already resonating with your audience.
Measurement that supports organic growth
Track a small set of KPIs weekly and monthly. Understanding the difference between Engagement vs Reach: What Matters for Nonprofits? is key, as chasing the wrong numbers can dilute your focus.
Week-to-week (operational)
Engagement rate (comments + shares + saves ÷ impressions).
Top-performing post and why (format, time, caption).
Monthly (outcome-focused)
Email sign-ups from social (conversion that matters).
Small donations or volunteer signups originated via social.
Traffic to key pages (program, donate, volunteer).
New community members (group joins, event RSVPs).
Set one simple conversion goal each month (e.g., +50 email signups) and align your Nonprofit Social Media Content Calendar to that goal. If reach grows but conversions don’t, sharpen CTAs and landing pages. If conversions grow but reach stalls, test small paid boosts or partnership amplification.
Content calendar template (minimal, high-impact)
Weekly rhythm (example for a small team):
Monday: Program story (Story → Insight → Micro-ask)
Wednesday: Behind-the-scenes mini post or volunteer spotlight
Friday: Conversation starter (question/poll) or event reminder
Weekend: Repurpose a clip or share community UGC
One monthly task: review the top 3 posts and plan two variations of the best format for the next month. For more on frequency, see the posting frequency guide.
Practical checklist to start tomorrow
- Pick one priority platform.
Define two audience segments and one conversion goal.
Build a 4-week content calendar using the Story → Insight → Micro-ask framework.
Create a 1-page consent form and start a story bank folder (photos, permission notes, 60-second videos).
Set a 15–30 minute daily engagement window and a 90-minute weekly content block.
Track one conversion in your spreadsheet (email signups from social).
If you want to build this into a broader effort, align it with your overall social media strategy for nonprofits and connect social goals to program outcomes.
Final Words
Nonprofit social growth is not a sprint or a contest for viral fame. It’s a disciplined system of storytelling, community-building, and measurement that amplifies the work you already do. Start small, focus on engagement, keep stories at the center, and build systems that survive staff turnover.
If capacity becomes the bottleneck, consider a short-term engagement with a professional who understands nonprofit social media marketing. That targeted support often produces practical systems you can run internally.
FAQs
What is an organic social media strategy?
It’s growing your audience and engagement without paid ads. You earn attention by building a community around valuable content that people want to share.
How to grow on social media organically?
Share authentic stories, ask questions to start conversations, and respond to every comment. Consistent, genuine interaction is the key to sustainable growth.
How to drive organic social media growth in 2026?
Focus on creating high-quality content that sparks conversation on a few select platforms. Algorithms reward real engagement, so building a tight-knit community is more effective than broad-casting messages.
How to create a successful social media strategy for nonprofits?
Focus on your mission and audience. Choose 1-2 key platforms, create consistent, valuable content, and engage with your community. Measure what matters, like comments and shares, not just followers.





